Low back pain is an aching discomfort that normally occurs in the lumbar portion of the spine. It is one of the most common health problems, and is the reason most drivers often give for taking time off work.
Low back pain may be the result of excessive strain on the lower back due to a poor posture, bad seating position when driving, being overweight, or having to do a lot of carrying or lifting of heavy loads. For a few people, persistent back pain may be due to arthritis.
More...
What is low back pain?
Back pain is usually caused by a mechanical disorder of one of the structures in or around the spine. The pain may be the result of damage to a ligament or muscle, or to one of the joints between adjacent vertebrae (bones of the spine).
Occasionally the pain is due to a slipped disc, a condition in which the spongy material between the vertebrae, bulges through its surrounding ligament and presses on adjacent spinal nerves. This nerve pressure causes pain in the back and also pain running down the back of the legs (sciatica).
Other causes of back pain include arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis (a disease of the joints) and, rarely, a tumour in the spinal column. It may also be caused by abdominal problems such as peptic ulcer, pancreatitis or aortic aneurism (localised dilation of the aorta).
In most cases, back pain goes away within a few days. It often improves before the doctor has arranged any tests, so the exact cause may not be confirmed. If the pain persists or keeps coming back, tests will be done to establish a diagnosis.

SYMPTOMS
- Pain that radiates from the back into a leg.
- Numbness or tingling sensations which occur in one or both legs.
- Weakness in a leg.
- Loss of control over bladder or bowel.
How is low back pain diagnosed and treated
Most episodes of low back pain can be resolved by resting the back for a few days. However, if low back pain is persistent or recurrent, the doctor's diagnosis can usually be made by means of a physical examination.
The physical examination includes testing neurological (nervous system) responses and muscle function. Other diagnostic studies may include taking a CT scan (a complex form of X-ray which gives a detailed cross-sectional image of a part of the body), or a myelogram (an X-ray of the back taken after an injection of a dye into the spine).
Bed rest for at least a few days only and followed by gentle movements. Painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants, heat pads / baths may be prescribed to help relieve muscle spasm.
Manipulation of the back by a doctor, physiotherapist or osteopath can be very effective, helping to relieve the pain and spasms in some cases.

WARNING
Anyone with severe back pain caused by an injury or fall, or who is unable to move, should be taken by ambulance to the nearest hospital.
Do not move the injured person as this should only be done by trained staff.
What can I do myself
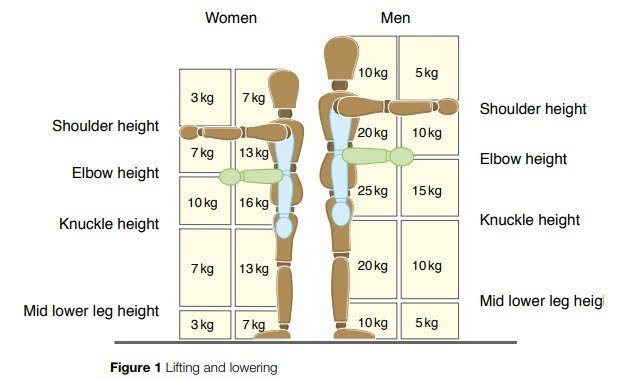
Factors that increase the risk of injury include the load being too heavy, large, difficult to grasp or unstable, the task being too strenuous or involving awkward postures or movements.
The working environment lacking sufficient space, having slippery, uneven or unstable floors, having extreme temperatures or poor lighting.
Employers are required to carry out risk assessments, and take action to protect workers from the risks of manual handling.
Prevention measures include:
• Designing and organising tasks to avoid manual handling completely, or at least restrict it.
• Using automation and lifting equipment.
• Organising manual handling tasks in a safe way, with loads split into smaller ones, and proper rest periods provided.
• Providing information and training to workers on tasks, and the use of equipment and correct handling techniques. (CPC Course)
Avoid prolonged sitting and keep the back mobile. Take a walk during your 4.5 hours rest periods and ensure your seat is correctly adjusted for your size.
Take regular exercise on your days of work and attempt to strengthening abdominal and back muscles. Swimming is excellent exercise for back pain. Using a back rub can also help control minor bouts of back pain.
Some people find relief from cold treatment with an ice pack.
For persistent backache, a gradual loss of excess weight will help reduce the weight-bearing load on the spine. Sleeping on a firm mattress and, for severe, chronic back pain, wearing a corset-like back brace can also help to ease the situation.
Reducing emotional stress if at all possible, can help, as many people unconsciously tighten their back muscles when they are worried or tense.
When should I see my doctor
Your doctor will examine your posture and the movements of your back when you are standing. You will then be asked to lie down so your back can be checked for areas of tenderness and muscle spasm. The nerve and muscle function in both legs will also be checked, as pressure on the spinal nerve can cause numbness or weakness.
Is low back pain dangerous
Low back pain is rarely dangerous. However, if the pain is accompanied by leg weakness, a feeling of numbness, or bladder or bowel problems, this indicates that there is pressure on one or more of the spinal nerves.
If the pain is caused by a disc prolapse or tumour, prolonged pressure on a spinal nerve will require surgery, as permanent nerve damage can result. You must see a doctor if the pain is persistent.
How can I avoid low back pain
- Maintain your ideal weight.
- Practice back and abdominal exercises.
- Wear flat or low shoes.
- Sleep on a firm mattress.
- When lifting, squat down in a knee-bend, pick up the object and hold it close. Keep your back upright, but not unnaturally straight. Slowly straighten your legs as you rise.
ALTERNATIVE TREATMENT
Many people with recurrent back pain have found relief by studying and following the Alexander Technique.
This is a system of posture adjustment and training for the correct movement of the spine, neck and limbs.
The technique is taught in individual classes.

